Full consciousness seems to involve the incremental awakening of the components of person-hood and identity. Recent research findings about the stages of recovery from anesthesia suggest that between the layer of ‘normal’ consciousness and deep sleep, certain intermediate “hubs” of perceptive experience are passed. Found in the cortex and the thalamus, these hubs are connected to the processing of instinct and emotion, and the awakening of conscious perception prior to content.
It seems that prior to forming identity as a person in time and space, we first experience fluid sensations of emotion and a sense of the here and the now without location or time. Could this be akin to the clarity of “Beginners’ Mind”, as referred to in Buddhism?
Anesthesia makes otherwise painful procedures possible by derailing a conscious brain, rendering it incapable of sensing or responding to a surgeon’s knife. But little research exists on what happens when the drugs wear off.
“I always found it remarkable that someone can recover from anesthesia, not only that you blink your eyes and can walk around, but you return to being yourself. So if you learned how to do something on Sunday and on Monday, you have surgery, and you wake up and you still know how to do it,” says Alexander Proekt, a visiting fellow in Don Pfaff’s Laboratory of Neurobiology and Behavior at Rockefeller University and an anesthesiologist at Weill Cornell Medical College. “It seemed like there ought to be some kind of guide or path for the system to follow.”
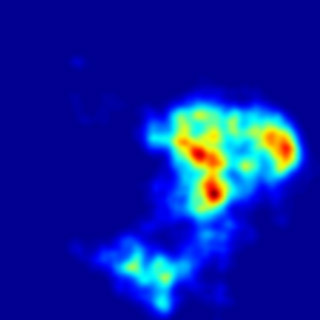
New findings suggest the anesthetized brain must pass through certain ‘way stations’ on the path back to consciousness. Above, the prevalence of particular clusters of brain activity states as recorded in rats that had been administered an anesthetic. The longest appear in red and the shortest in yellow and green.
The obvious explanation is that as the anesthetic washes out of the body, electrical activity in the brain gradually returns to its conscious patterns. However, new research by Proekt and colleagues suggests the trip back is not so simple.
“Using statistical analysis, our research shows that the recovery from deep anesthesia is not a smooth, linear process. Instead, there are dynamic ‘way stations’ or states of activity the brain must temporarily occupy on the way to full recovery,” Pfaff says. “These results have implications for understanding how someone’s ability to recover consciousness can be disrupted by, for example, brain injury.”
Proekt, along with former postdoc Andrew Hudson, now an assistant professor in anesthesiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Diany Paola Calderon, a research associate in the lab, put rats “under” using the common medical and veterinary anesthetic isoflurane. As the rats recovered, the team monitored the electrical potential outside neurons, known as local field potentials (LFPs), in particular parts of the brain known, from previous elecrophysiological and pharmacological studies, to be associated with wakefulness and anesthesia. These recordings gave them a sensitive handle on the activities of whole groups of neurons in particular parts of the thalamus and cortex.
In the awake brain, of both humans and rats, neurons generate electrical voltage that oscillates. Many of these oscillations together form a signal that appears as a squiggly line on a recording of brain activity, such as an LFP. When someone is asleep, under anesthesia, or in a coma, these oscillations occur more slowly, or at a low frequency. When he or she is awake, they speed up. The researchers examined the recordings from the rats’ brains to figure out how the electrical activity in these regions changed as they moved from anesthetized to awake.
 “Recordings from each animal wound up having particular features that spontaneously appeared, suggesting their brain activity was abruptly transitioning through particular states,” Hudson says. “We analyzed the probability of a brain jumping from one state to another, and we found that certain states act as hubs through which the brain must pass to continue on its way to consciousness.” While the electrical activity in all the rats’ brains passed through these hubs, the precise path back to consciousness was not the same each time, the team reports today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Recordings from each animal wound up having particular features that spontaneously appeared, suggesting their brain activity was abruptly transitioning through particular states,” Hudson says. “We analyzed the probability of a brain jumping from one state to another, and we found that certain states act as hubs through which the brain must pass to continue on its way to consciousness.” While the electrical activity in all the rats’ brains passed through these hubs, the precise path back to consciousness was not the same each time, the team reports today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“These results suggest there is indeed an intrinsic way in which the unconscious brain finds its way back to consciousness. The anesthetic is just a tool for severely reducing brain activity in a way in which we can control,” Hudson says.
In other scenarios, including coma caused by brain injury or neurological disease, the disruption to brain activity cannot be controlled, making these states much more difficult to study. However, the team’s results may help explain what is going on in these cases. “Maybe a pathway has shut down, or a brain structure that was key for full consciousness is no longer working. We don’t know yet, but our results suggest the possibility that under certain circumstances, someone may be theoretically capable of returning to consciousness but, due to the inability to transition through the hubs we have identified, his or her brain is unable to navigate the way back,” Calderon says.












